
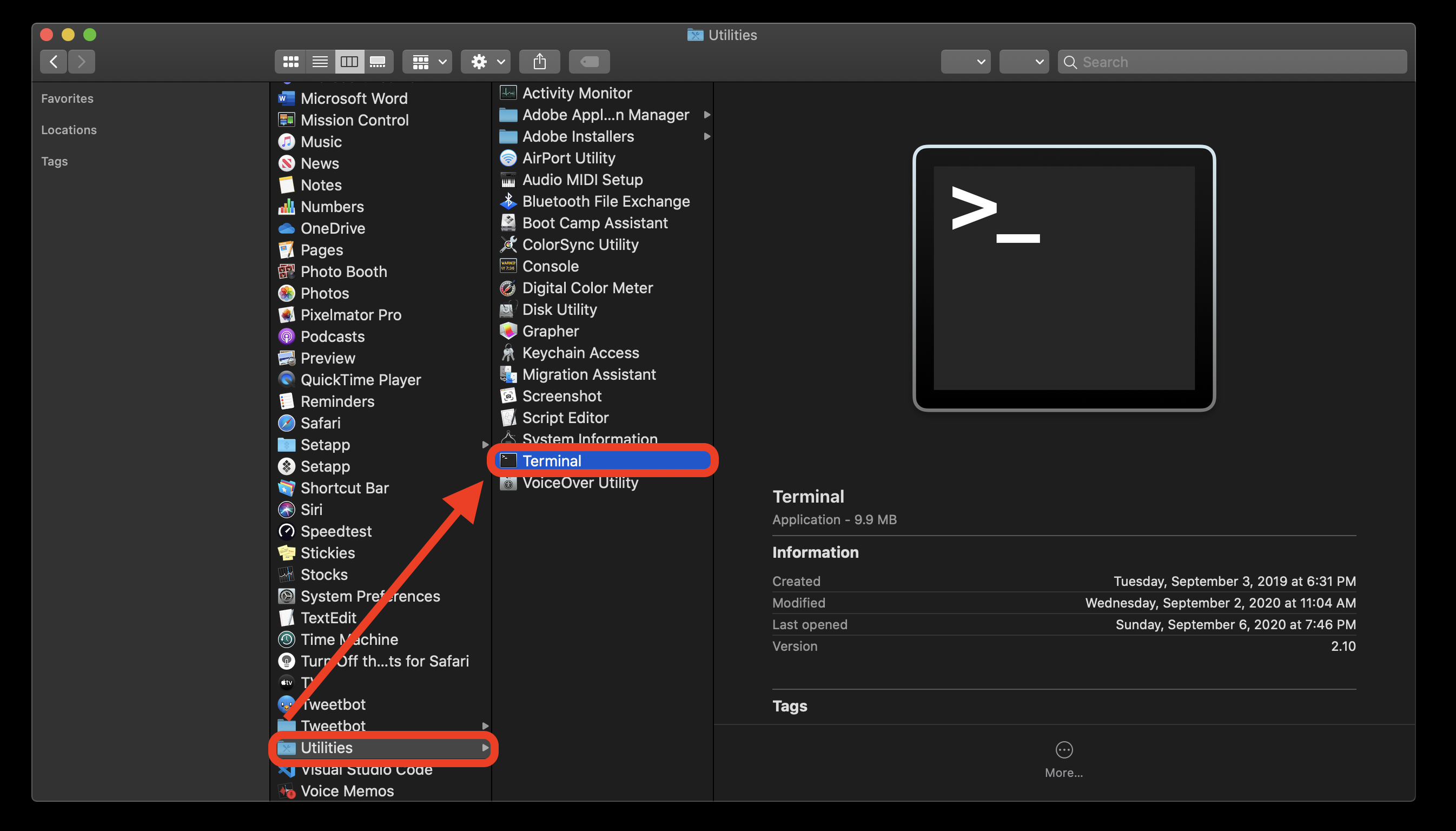
- #Open terminal from finder how to#
- #Open terminal from finder mac os x#
- #Open terminal from finder full#
#Open terminal from finder how to#
In summary, if you wanted to see how to run/execute a Unix shell script from the MacOS Finder, I hope these examples are helpful. (The pwd command will just list the user’s home directory.) Summary
#Open terminal from finder full#
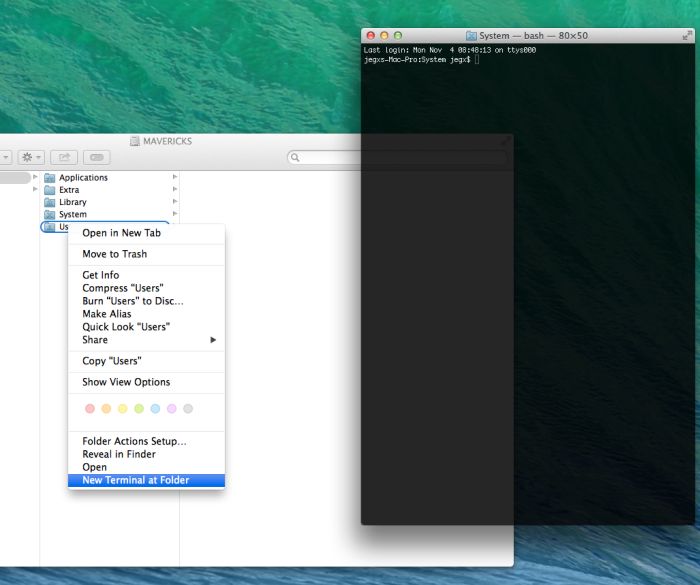
If you need to get the full path of the directory where your script was run from, use this command:Īfter that line executes, the variable DIRNAME will contain the full path to the directory where the user executed your script in the Finder. You should see a Terminal window open, with the output from the commands shown in the Terminal window. The command to open the current folder from terminal is: Open. Now, when you're in Finder, just right-click a folder.

Find 'New Terminal at Folder' in the settings and click the box. Now go to the Finder, navigate to the directory where this script is located, and double-click the icon for this file. Open current folder in Finder from Terminal. Head into System Preferences and select Keyboard > Shortcuts > Services. Put some simple commands in the file, like this:
#Open terminal from finder mac os x#
Simple exampleĪs a simple example of this, create a file named mand somewhere on your Mac OS X filesystem, such as the Desktop, or a temp folder somewhere. I run a top command in a script so she can confirm that this is the problem. She has an HP printer attached to her Mac, and from time to time the printer goes nuts and decides to eat the CPU. I did this recently for one of my sisters. When it’s finished, the Terminal will display a “Process Completed” message, and the user can close the Terminal.
Now, when someone double-clicks your script in the Mac Finder, the script will open a new Mac Terminal window, and then run the script inside that window. You can also leave out the usual #!/bin/sh part on the first line. GitHub - Ji4n1ng/OpenInTerminal: Finder Toolbar app. Then make it executable, such as by running chmod from the MacOS Terminal: Finder Toolbar app for macOS to open the current directory in Terminal, iTerm, Hyper or Alacritty. command extension and (b) make it executable.įor example, just name your Mac/Unix script like this: Solution: If you ever want to create a Unix shell script that you can give to someone else so they can double-click it and run it through the Mac OS X Finder, all you have to do is (a) name the file with the. You can open Get info on the Terminal app in the Utilities folder, and drag its icon to the top-left small icon to assign that icon to our new little app.įinally keep the ⌘ command key pressed and drag the app in the Finder toolbar.MacOS Finder FAQ: Is there a way that I can execute a custom Unix shell script from the Mac Finder? Save this application in the Applications folder and then click Get Info to change its icon. Then we open the Terminal app and we run the cd command to go into that folder. Which basically gets the current opened folder absolute path and stores it to the myPath variable.

There are also a 'lite' versions for either opening the directory in the terminal app or in the text editor with a single button. Most terminal apps and text editors are supported, including iTerm. The first runs osascript (which is a script to run AppleScript) with the following AppleScript tell application "Finder" set myPath to (POSIX path of (target of front window as alias)) end tell This app adds a menu to the Finder toolbar which opens the current directory in your default terminal app or your preferred text editor. If you prefer you can use “Run Shell Script” instead, and write this bash script: osascript -e ' tell application "Finder" set myPath to (POSIX path of (target of front window as alias)) end tell tell application "Terminal" do script "cd " & myPath activate end tell ' Search for “Run AppleScript” in the list of actions, and paste these lines: on run tell application "Finder" set myPath to ( POSIX path of (target of front window as alias )) end tell tell application "Terminal" do script "cd " & myPath activate end tell return input end run
I decided to make it easy by adding an “Open in Terminal” icon in the Finder: Then, you can either double-click or tap the Terminal. Let’s say I’m in the Finder, I open a folder and I want to open it in the Terminal. To open Spotlight, you can use the default keyboard shortcut Command () - Spacebar.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
